BACK
Linear programming is the process of taking various linear inequalities relating to some situation, and finding the "best" value obtainable under those conditions. A typical example would be taking the limitations of materials and labor, and then determining the "best" production levels for maximal profits under those conditions.
In "real life", linear programming
is part of a very important area of mathematics called "optimization
techniques". This field of study (or at least the applied results
of it) are used every day in the organization and allocation of resources.
These "real life" systems can have dozens or hundreds of variables,
or more. In algebra, though, you'll only work with the simple (and graphable)
two-variable linear case.
The general process for solving linear-programming
exercises is to graph the inequalities (called the "constraints")
to form a walled-off area on the x,y-plane
(called the "feasibility region"). Then you figure out the coordinates
of the corners of this feasibility region (that is, you find the intersection
points of the various pairs of lines), and test these corner points in
the formula (called the "optimization equation") for which you're
trying to find the highest or lowest value.
- Find the maximal and minimal value of z = 3x + 4y subject to the following constraints:
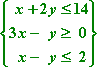
The three inequalities in the curly braces
are the constraints. The area of the plane that they mark off will be
the feasibility region. The formula "z
= 3x + 4y" is
the optimization equation. I need to find the (x,
y) corner points of the feasibility
region that return the largest and smallest values of z.
My first step is to solve each inequality
for the more-easily graphed equivalent forms:
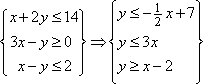
- It's easy to graph
the system: 00
- 6-2011 All Rig
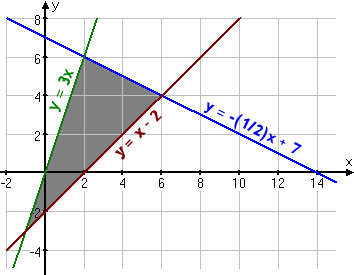
- To find the corner points -- which aren't
always clear from the graph -- I'll pair the lines (thus forming a system
of linear equations) and solve:
y
= –( 1/2 )x
+ 7y
= 3x
|
y
= –( 1/2 )x
+ 7y
= x
– 2
|
y
= 3x
y = x – 2 |
–( 1/2
)x
+ 7 = 3x–x
+ 14 = 6x14
= 7x
2 = x
y
= 3(2) = 6
|
–( 1/2
)x
+ 7 = x
– 2
–x + 14 = 2x – 4 18 = 3x 6 = x
y
= (6) – 2 = 4
|
3x
= x
– 2
2x = –2x = –1
y
= 3(–1) = –3
|
corner point at
(2, 6)
|
corner point at (6,
4)
|
corner pt. at (–1,
–3)
|
- So the corner points are (2,
6), (6,
4), and (–1,
–3).
Somebody really smart proved that, for linear systems like this, the maximum and minimum values of the optimization equation will always be on the corners of the feasibility region. So, to find the solution to this exercise, I only need to plug these three points into "z = 3x + 4y".
- (2, 6): z
= 3(2) + 4(6) = 6 + 24 = 30
(6, 4): z = 3(6) + 4(4) = 18 + 16 = 34
(–1, –3): z = 3(–1) + 4(–3) = –3 – 12 = –15
- Then the
maximum of z
= 34 occurs
at (6,
4),
and the minimum of z = –15 occurs at (–1, –3).
- Given the following constraints, maximize and minimize the value of z = –0.4x + 3.2y.
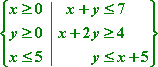
- First I'll solve the fourth and fifth
constraints for easier graphing:
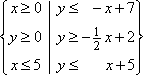
- The feasibility region looks like this:
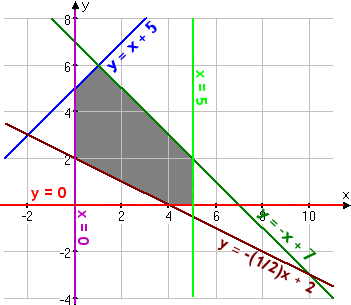
- From the graph, I can see which lines
cross to form the corners, so I know which lines to pair up in order
to verify the coordinates. I'll start at the "top" of the
shaded area and work my way clockwise around the edges:
y
= –x
+ 7y
= x
+ 5
|
y
= –x + 7x = 5
|
x
= 5y
= 0
|
–x
+ 7 = x
+ 5
2 = 2x 1 = x
y
= (1) + 5 = 6
|
y
= –(5) + 7 = 2
|
[nothing to do]
|
corner at
(1, 6)
|
corner at (5,
2)
|
corner at (5,
0)
|
y
= 0y
= –( 1/2 )x
+ 2
|
y
= –( 1/2 )x
+ 2x
= 0
|
x
= 0y
= x
+ 5
|
–( 1/2
)x + 2 = 0
2 = (1/2)x 4 = x |
y
= –( 1/2 )(0) + 2
y = 0 + 2 y = 2 |
y
= (0) + 5 = 5
|
corner at
(4, 0)
|
corner at
(0, 2)
|
corner at
(0, 5)
|
- Now I'll plug each corner point into
the optimization equation, z
= –0.4x + 3.2y:
- (1, 6): z =
–0.4(1) + 3.2(6) = –0.4 + 19.2 = 18.8
(5, 2): z = –0.4(5) + 3.2(2) = –2.0 + 6.4 = 4.4
(5, 0): z = –0.4(5) + 3.2(0) = –2.0 + 0.0 = –2.0
(4, 0): z = –0.4(4) + 3.2(0) = –1.6 + 0.0 = –1.6
(0, 2): z = –0.4(0) + 3.2(2) = –0.0 + 6.4 = 6.4
(0, 5): z = –0.4(0) + 3.2(5) = –0.0 + 16.0 = 16.0
- Then the
maximum is 18.8
at (1,
6) and the
minimum is –2
at (5,
0).
No comments:
Post a Comment